Our Framework
Spreading our passion for education
This Framework for the Systemic Improvement of Educational Institutions (SIEDI) was conceived to be a complete and detailed referent for schools looking to transform themselves with the main goal of better responding to each of their student’s educational needs.
The development of the SIEDI Framework is our response to the need for an educational innovation reference focused on the person. In the education world, there’s a wide
variety of available methodologies, technologies, curriculums, and pedagogical approaches to choose from, it can be a real challenge to choose the ones to be implemented in a school.
As a result of the importance we acknowledge language has, and in order to build a common ground of understanding, we will explain how some of the main concepts and the meaning they hold to us in the SIEDI Framework.
Educational Innovation
Changes made to the educational system and process with the intention of better fostering the learning of the students always considering and responding to each unique and whole person.
Learning Experience
Integration of the environment, time, activity, resources, etc. in which the student should fully engage to internalize the selected knowledge, or develop the intended skill.
Educational Process
Series of concatenated experiences guided and/or designed by the teacher to foster each student’s learning.
Skill Development
Personal and social process of achieving an ability mastery so that is applicable in different world contexts. It’s a process that involves not just the ability, but also the sensibility to when it’s needed, and the motivation to use it.
Learning
Personal and social process of internalizing knowledge that should reach deep levels of understanding so that is connected and applicable in different world contexts. It’s a process closely related to the process of thinking, since they are both cause and effect of each other.
Student
Person enrolled in school to learn. Leader of his/her learning process and to do so, engages his/her body, emotions, intelligence and will.
The SIEDI Framework is built on 6 blocks which entail the structure and working of the complex system that is a school. They are intertwined and as a consequence, every change in any given axis will impact the others. The transformation process of an educational institution towards a person-centered innovation always implies all 6 blocks.
Nowadays schools face a big challenge to allow and foster new ways to envision, plan and develop the educational processes. Schools recognizing the need to innovate can find in the SIEDI Framework guide and support for their transformation process.
The SIEDI Framework helps schools analyze their current stance and so, they see “the whole picture”, pinpointing the essential elements of the educational process. The first step always is knowing the starting point, but being there is not enough to get going, that’s why the framework is built as a detailed scale that clarifies the path as each school defines their improvement route. Besides, the SIEDI Framework allows and encourages constant evaluation to keep all investments of energy, time, money, etc., on track.
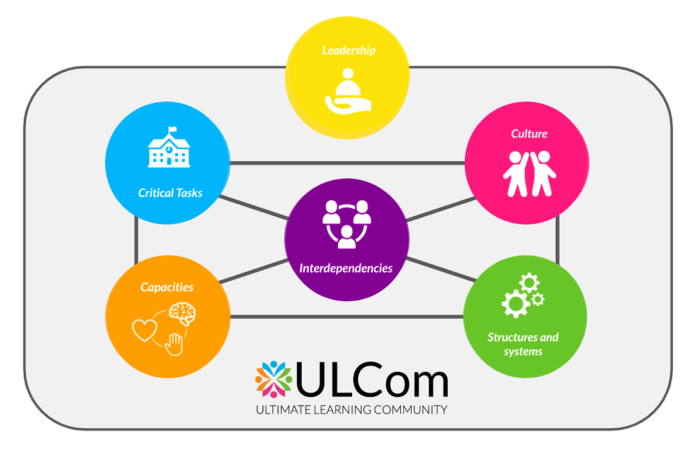
These 6 blocks reflect a school’s reality and its interactions, they make visible its way of working in detail.
Each one of the blocks is comprised of a series of elements, which group together some aspects.
Together the blocks are the reflection of the school, as they were conceived to help bring to light the priorities, values, and beliefs both stated as ideals, and the actual ones guiding the daily life at the school. Thus, they are dynamic, changing and influencing one another.

Critical Tasks
This block considers the work in the institution, every task that needs to be done to accomplish the organization's essential work. In education these refer to the instruction, the curriculum, the teaching, and the learning.

Interdependencies
This block refers to the collaboration and coordination needed between teachers across subjects and grade levels, or with stakeholders outside the institution as they effectively carry out the work of the teaching-learning process.

Culture
This block considers the norms, values, and beliefs of the people in the organization, as well as the resulting behaviors and artifacts that represent these beliefs.

Capacities
This block implies the skills, capacities, and attitudes of the people carrying out the institution's critical tasks: teachers, administrators, support individuals, and other employees.

Structures and Systems
This block analyzes the roles, responsibilities, formal reporting structure, incentives, building(s), equipment, technology, schedule, metrics, safety, and the date systems of the institution.

Leadership
This block implies the style and competencies of the leader and her ir his senior leadership team.